Air pollution is a pervasive and often invisible threat that affects millions of people worldwide. It is the single largest environmental health risk in Europe and a major cause of premature death and disease. The World Health Organization estimates that 99% of the global population breathes polluted air, causing around seven million deaths each year. The issue is particularly severe in Asia and Africa, where rapid industrialization and urbanization have led to significant air quality deterioration.

Impact on Health
Air pollution has severe health implications, including:
Cardiovascular Disease: Air pollution increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. It is responsible for 25% of all cardiovascular disease deaths, equivalent to more than 3.5 million deaths every year.
Respiratory Diseases: Air pollution exacerbates respiratory conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It also increases the risk of lung cancer and other respiratory cancers.
Neurological Disorders: Exposure to air pollution has been linked to neurological disorders such as dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease.
Birth Outcomes: Air pollution exposure during pregnancy is associated with low birth weight, preterm birth, and other adverse birth outcomes.
Solutions
To mitigate the health impacts of air pollution, several solutions are necessary:
Cleaner Energy: Transitioning to cleaner energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can significantly reduce air pollution emissions.
Energy Efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in buildings and industries can also reduce emissions.
Transportation: Promoting cleaner transportation options, such as electric vehicles and public transportation, can reduce emissions.
Air Quality Monitoring: Implementing air quality monitoring systems can help track and manage pollution levels.
Community Engagement: Educating communities about the health risks of air pollution and involving them in mitigation efforts can foster greater awareness and action.
Innovative Approaches
Recent innovations have made air pollution more visible and accessible to the general public:
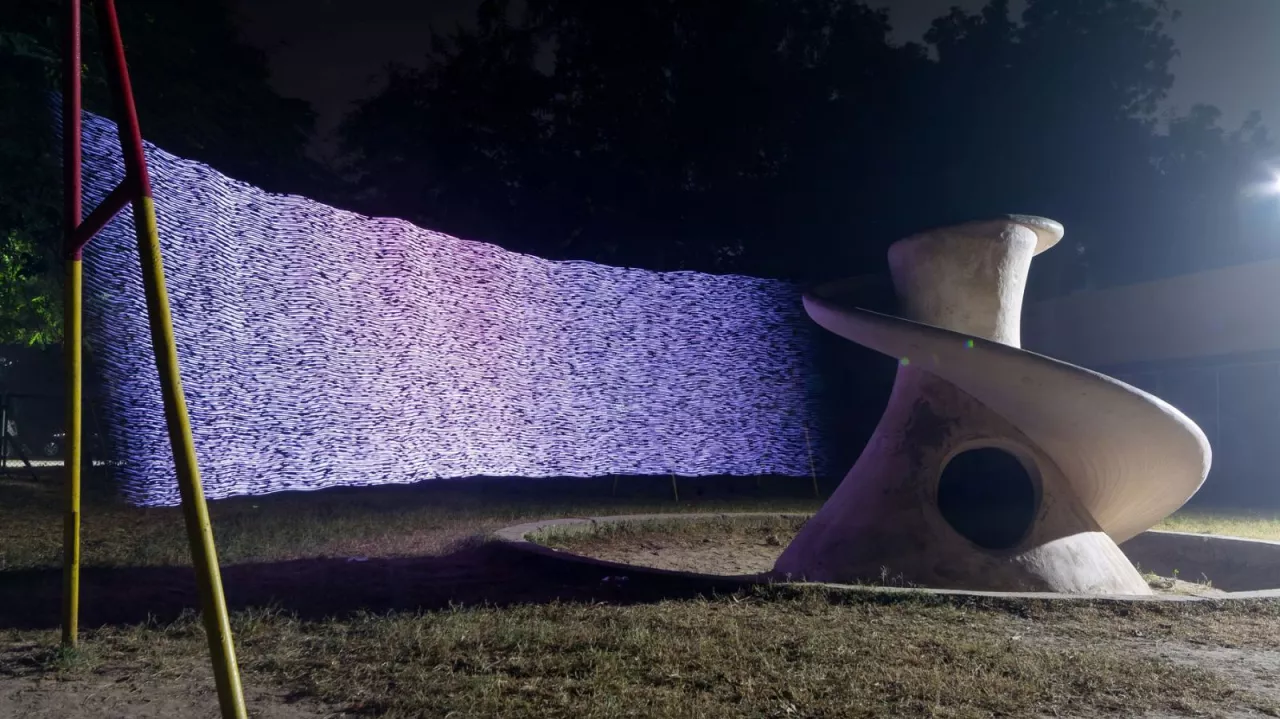
Digital Light Painting: The “Air of the Anthropocene” project uses digital light painting to create striking photographic evidence of pollution levels in cities across Ethiopia, India, and the UK. This approach makes air pollution visible and sparks crucial discussions within local communities.
Community-Engaged Research: The NIEHS supports community-engaged research and citizen science initiatives that involve residents in tracking air pollution and developing solutions.
Air pollution is a pressing global health crisis that requires immediate attention and action. By understanding the health impacts of air pollution and implementing effective solutions, we can reduce the burden of disease and improve the quality of life for millions of people worldwide.