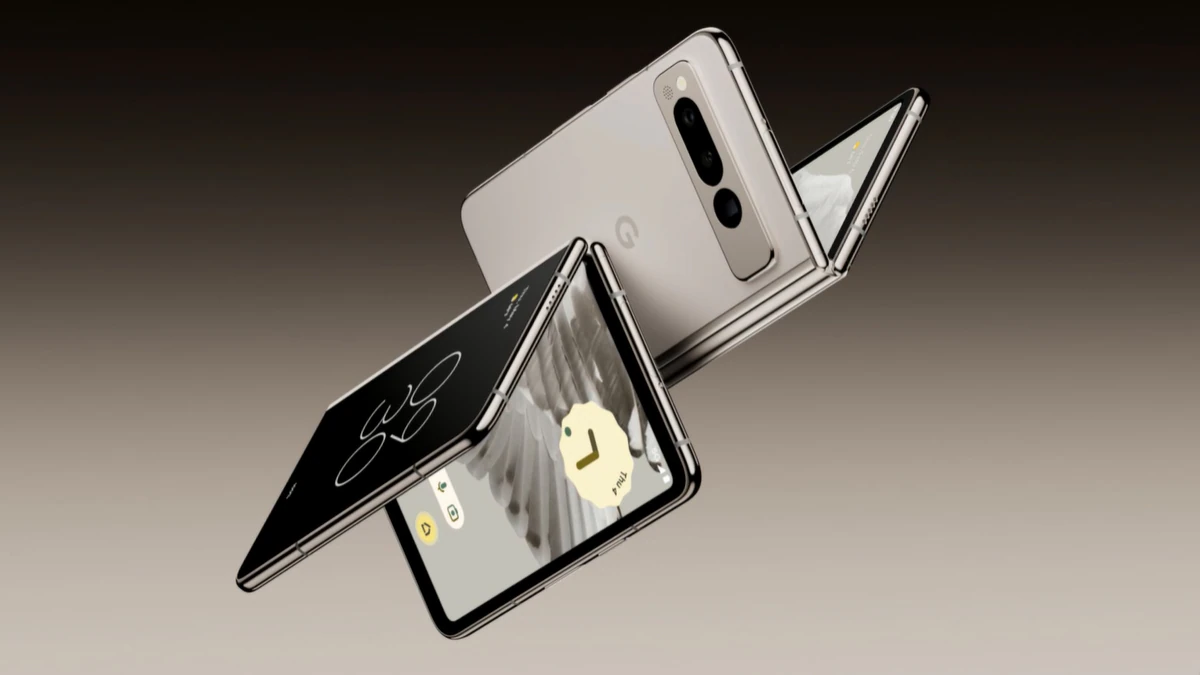
Google is gearing up to launch its next foldable phone and it is gonna be the Pixel Fold 2. The device will come with some significant upgrades, particularly in terms of its display size. According to industry analyst Ross Young from Countepoint Research, who was formerly with DSCC, the Pixel Fold 2 will feature a larger screen than previously leaked.
![]()
The device will feature flattened sides and a revamped overall profile, drawing inspiration from OnePlus Open. The bezels have been significantly reduced, contributing to a sleeker and more aesthetically pleasing appearance.
Initial leaks suggested a 7.9-inch inner foldable screen for the Pixel Fold 2. Young’s recent post on X (formerly Twitter) reveals that the inner flexible panel will actually measure 8.02 inches, marking a substantial increase compared to the 7.6-inch OLED panel found in the first-gen Google Pixel Fold.
Additionally, while the cover screen was initially rumored to be 6.4 inches, it will now measure 6.29 inches, still a notable improvement over the 5.8-inch outer display of the current version. Alongside the display enhancements, the Pixel Fold 2’s design is also undergoing changes.
With a slim profile measuring just 10.54mm, the Pixel Fold 2 is expected to set a new standards for thinness in the foldable phone segment. Google is rumored to be considering the next-gen Tensor G4 chip to power the device.
Optimizing apps for expansive displays, such as the 8-inch screen of the Pixel Fold 2, would not only enhance their visual appeal but also benefit the overall user experience. This optimization could also breathe new life into Android tablets, which have long been overlooked.
what consumers are eagerly anticipating is improved optimization of apps for larger screens. Apple has taken steps to optimize its Apple Music app for foldable phones, hinting at the potential for further innovation in the realm of foldable devices.