Rivers are important for life on Earth. A recent study led by NASA gives new information about how much water is in Earth’s rivers. Before this study, it was hard to know exactly how much water was in rivers because of limited ways to measure it. But now, using new methods, scientists estimate that all of Earth’s rivers combined hold about 539 cubic miles (2,246 cubic kilometers) of water.
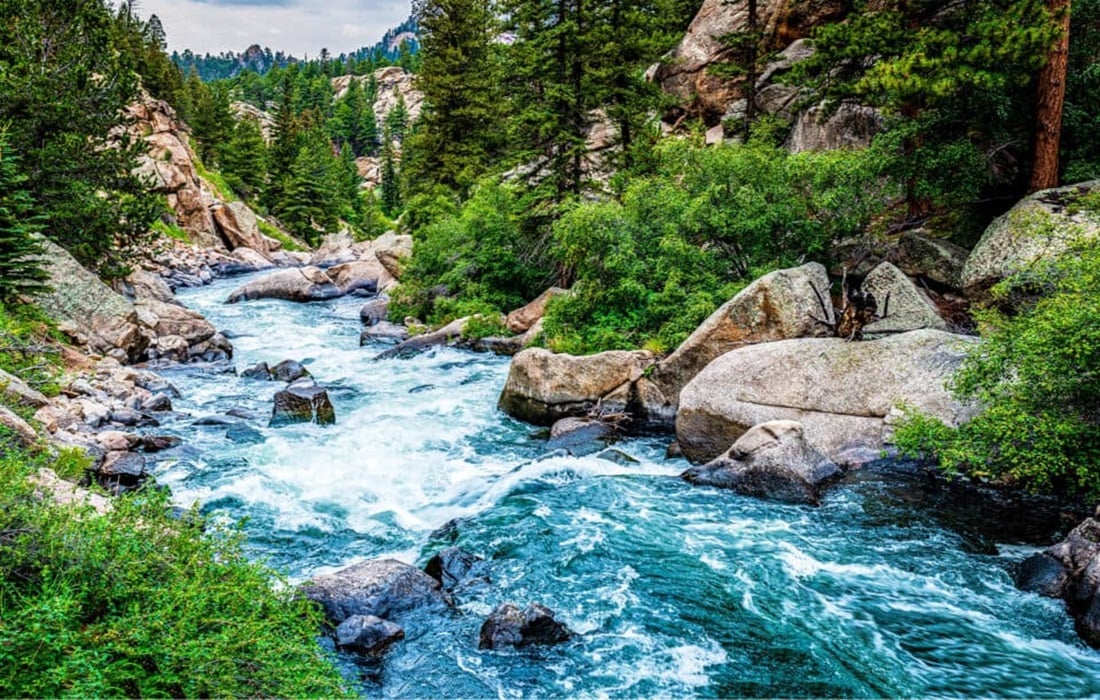

Even though this may seem like a small amount compared to all the water on Earth, it’s still very important. Rivers help ecosystems, farms, and people all around the world. This information helps us better manage our water resources.
To figure out how much water is in rivers, scientists used special computer models and real measurements from river sensors. They looked at around 3 million parts of rivers all over the world to get a good picture of how rivers work.
Sometimes, the computer models didn’t match the real measurements exactly. This showed that the models needed to be improved. By making these improvements, scientists can get better at predicting how much water is in rivers.
Knowing how much water is in rivers helps us understand how water moves around the Earth. It also helps us plan for how to use water better, especially as the climate changes. One river basin that stands out is the Amazon River in South America. It holds about 38% of all the water in Earth’s rivers. This shows how important the Amazon is for our planet’s water system.
The Amazon River also sends a lot of water into the oceans. In fact, it’s responsible for about 18% of all the water that rivers put into the oceans. This affects the saltiness of the oceans and even the climate.
The study also points out some areas where water is being used too much. Places like the Colorado River in the United States and the Murray-Darling River in Australia are using too much water. This is a problem because it can lead to shortages of water for people and ecosystems.
Scientists hope that new satellites, like NASA’s SWOT satellite, will help us learn even more about Earth’s rivers. SWOT can measure water levels in rivers from space, which will give us even more information to help manage our water better.