The Caspian Sea is a unique place that can be called both a lake and a sea. Even though its water is salty like the ocean, it’s not as salty. It can also be considered a lake because it’s not connected to any sea or ocean. Situated between the Caucasus Mountains to the east and grasslands to the west, it covers a vast area of 371,000 square kilometers.
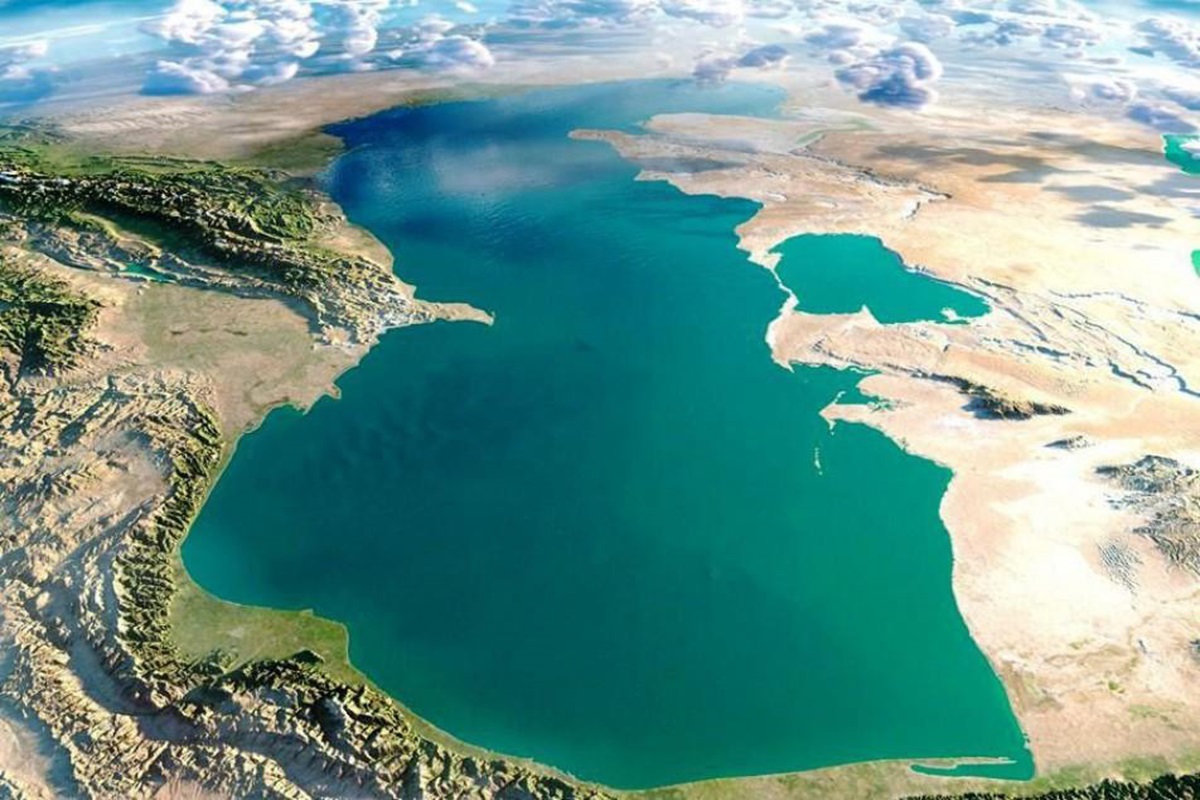

The Caspian Sea is shared by five countries: Kazakhstan, Russia, Azerbaijan, Iran, and Turkmenistan. About 5.5 million years ago, it completely separated into its own basin. Currently, the Caspian Sea has a salinity of 1.2 percent. The Volga River is its primary water source, and the South Caspian, with an average depth of 3,300 feet, contains 66 percent of the sea’s water. The sea’s islands are mostly close to the coast.
Many bird species use the Caspian Sea as a temporary residence, and Baku, the capital of Azerbaijan, is located near its shores. A unique species, the Caspian seal, is found only in this region. Once numbering one million, the seals have decreased to 100,000 due to human hunting. Other whale fish species that were once present in the Caspian Sea have disappeared.
Surprisingly, special species of tigers, leopards, and lions, such as the Caspian tiger and Asiatic lion, were found in the Caspian region. The Persian cheetah is also a unique inhabitant. The Caspian Sea is home to specific sturgeon fish species not found anywhere else.
Iran’s part of the Caspian Sea holds significant oil reserves, estimated at 150 billion barrels. Iran regularly imports crude oil from this region. Russia’s part of the Caspian Sea contains reserves of fuel oil and natural gas.
Unfortunately, the construction of factories around the Caspian Sea has led to the dumping of waste, resulting in the loss of marine biodiversity. In response, the five littoral countries formed an organization and hold the Caspian Conference every two years to address these environmental challenges.