Creating artificial suns may seem confusing to many people, but these are not like the Sun we see in the sky. They won’t be placed up there and won’t emit heat to reach us. Instead, they are produced in nuclear fusion reactors. To make these artificial suns, scientists need hydrogen and deuterium to react. This process is entirely environmentally friendly and has been studied for a long time.
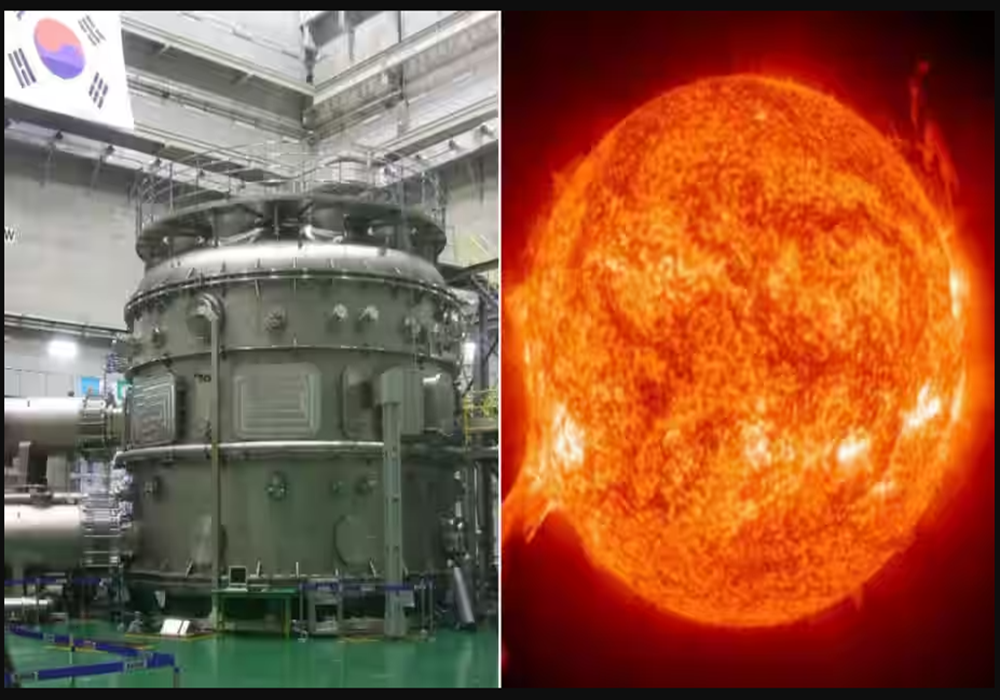
Recently, South Korean nuclear scientists achieved a remarkable feat by reaching a temperature of 100 million degrees Celsius, setting a world record. No other country has been able to achieve such a high temperature before. Nuclear fusion could become a crucial source of clean energy in the future world, and South Korean scientists have made significant progress in this regard.
They have successfully reached temperatures in the tens of millions of degrees Celsius and aim to break previous records. While high temperatures have been achieved in the past, they usually lasted for only around 30 seconds. However, South Korean scientists managed to maintain the temperature for 48 seconds this time.
During nuclear fusion experiments in the artificial sun, this temperature reaches 7 times that of the Sun’s core, which is around 15 million degrees Celsius. This achievement is considered a significant milestone for the future by South Korean scientists.
Other countries like China, America, and France are also working on developing artificial suns. This process generates a tremendous amount of energy, and scientists believe it could help solve climate problems because it’s environmentally friendly. In nuclear fusion, a lot of energy can be produced without causing carbon pollution.
Leave a Reply